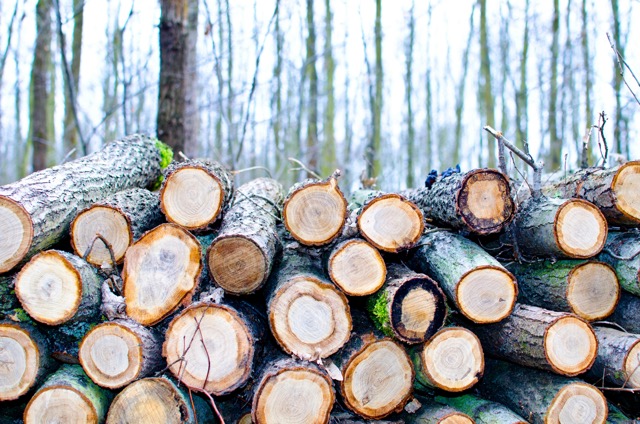
Wood has been one of the oldest and most versatile building and decorative materials in human history. Its durability, workability, and aesthetic appeal have made it indispensable in both traditional and modern architecture. However, “wood” is a broad term that covers a wide variety of types, each with unique properties. The most significant division comes down to hardwood and softwood.
So, what are the key differences between hardwood and softwood? Which is more durable, which is more affordable, and which should be chosen for furniture, flooring, or construction? In this guide, we will explore all of these questions in detail.
1. Definition of Hardwood and Softwood
Hardwood:
- Derived from broad-leaved, usually deciduous trees.
- Has a denser cellular structure, making it heavier and more durable.
- Common examples include oak, walnut, beech, cherry, mahogany, and maple.
Softwood:
- Comes from coniferous, needle-leaved trees, most of which are evergreen.
- Grows faster, is lighter, and easier to process.
- Common examples include pine, spruce, fir, and cedar.
Note: The terms “hard” and “soft” do not always refer to the actual hardness of the wood. For instance, some softwoods can be harder than certain hardwoods. The classification is botanical, not purely mechanical.
2. Density and Durability
- Hardwoods are denser, making them more resistant to scratches, dents, and external impacts. They are long-lasting and ideal for flooring, high-quality furniture, and outdoor applications.
- Softwoods are lighter with lower density, which makes them easier to work with but less resistant to wear and tear. They are often used in construction materials, roof structures, and temporary structures.
3. Aesthetic Appearance and Grain
- Hardwoods offer detailed grain patterns and a rich variety of tones, which add decorative value. Oak and walnut, for example, are sought-after in luxury furniture because of their elegant and timeless look.
- Softwoods have smoother and more uniform textures, making them ideal for painted or varnished finishes. They fit well into mass production and cost-efficient projects.
4. Applications in Daily Life
Hardwood Applications:
- Premium indoor and outdoor furniture
- Flooring and parquet
- Decorative items and fine woodworking
- Luxury interior design
Softwood Applications:
- Construction beams and frameworks
- Roofing, cladding, and structural elements
- Doors, windows, and paneling
- Affordable, mass-produced furniture
5. Workability
- Softwoods are much easier to cut, sand, and shape due to their lower density. This makes them highly practical for carpentry and large-scale construction.
- Hardwoods require more effort, specialized tools, and craftsmanship. However, once processed, they produce more durable and sophisticated results.
6. Cost and Affordability
- Hardwoods are usually more expensive. They grow slower, are less abundant, and are often considered premium materials. Species like walnut and mahogany are particularly costly.
- Softwoods are more affordable thanks to their fast growth and wide availability. For large-scale projects, they provide significant cost savings.
7. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
- Softwoods grow faster and can be replanted more easily, making them more sustainable in managed forestry.
- Hardwoods take longer to grow and are less abundant. However, due to their durability, they can last much longer in use, balancing their environmental impact.
8. Fire Resistance
- Hardwoods are denser, which makes them burn more slowly and resist fire better. This quality makes them ideal for certain outdoor and structural applications.
- Softwoods ignite more easily and burn faster, so they require additional fire safety measures in construction.
9. Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
- Hardwoods: Their density makes them better at insulating against both heat and sound. This is why they are popular in flooring and interior paneling.
- Softwoods: While not as effective in insulation, they are lightweight and flexible, making them useful for structural frameworks.
10. Examples of Hardwood and Softwood Species
Hardwoods:
- Oak
- Walnut
- Beech
- Cherry
- Mahogany
- Maple
Softwoods:
- Pine
- Spruce
- Fir
- Cedar
11. Historical Usage
- Hardwoods have historically been associated with wealth and prestige. They were used in palaces, cathedrals, and fine antique furniture that still holds value today.
- Softwoods have been favored in shipbuilding, construction, and everyday utilitarian objects due to their abundance and practicality.
12. Which Is Better: Hardwood or Softwood?
There is no single answer—it depends on the intended use:
- For luxury, long-lasting furniture, and flooring, hardwood is the best choice.
- For cost-effective construction and large projects, softwood is more suitable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Which is more durable: hardwood or softwood?
In general, hardwoods are more durable. However, some softwoods can also provide sufficient strength depending on the intended use.
Which type of wood is more expensive?
Hardwoods are usually more expensive because they grow slower and are less abundant. Softwoods are more affordable and widely available.
Which type is better for furniture?
For long-lasting and aesthetic furniture, hardwoods are preferred. For budget-friendly or lightweight furniture, softwoods are a better option.
Which is more eco-friendly?
Softwoods, obtained from sustainably managed forests, are more eco-friendly due to their faster growth cycle. Hardwoods can also be sustainable when responsibly sourced.
Which is easier to work with: hardwood or softwood?
Softwoods are easier to cut, shape, and machine because of their looser grain structure. Hardwoods are tougher and require more advanced tools.
Which is more commonly used in interior design?
Hardwoods are more popular in interior design because of their natural aesthetics, rich colors, and durability. Softwoods are often used in structural elements and cost-effective projects.
How long does hardwood last compared to softwood?
With proper care, hardwood furniture and flooring can last 50 years or more. Softwoods usually last around 15–25 years depending on usage.
What are the most common types of hardwood and softwood?
Hardwoods: Oak, walnut, mahogany, teak, and beech, Softwoods: Pine, spruce, and fir.
Which is better in terms of cost/performance?
Softwoods are more economical in the short term. However, hardwoods provide better long-term value due to their durability and premium look.
Which wood types are more suitable for outdoor use?
Teak, oak, and mahogany are highly durable and naturally resistant to outdoor conditions. Softwoods can be used outdoors only if treated with preservatives.
The differences between hardwood and softwood come down to density, durability, aesthetics, price, environmental impact, and usage areas.
Hardwoods bring strength, elegance, and longevity, making them the material of choice for premium applications. Softwoods, on the other hand, offer affordability, versatility, and sustainability for everyday use and large-scale projects.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your budget, project needs, and design preferences.